Assignment Writing Guidelines
Are You looking for useful guides, formats & structures for academic assignment writing and language skills check out our range of study skills resources.
Academic Writing
Three main purposes for YOU:
- Assessment
- Learning
- Adopting the language associated with the subject area (jargon)
Academic Writing
Three main purposes for us:
- That you demonstrate your understanding
- That you undertake relevant readings
- That you become comfortable using a formal academic writing style and proper use of the Harvard referencing system
Assessment Criteria
- Your unit contains Assessment Criteria (AC) which specify the standard you are expected to meet to demonstrate that you have achieved the required criterion.
- You need to ‘ACHIEVE’ each of the Pass Assessment Criteria.
- If one of the Pass Assessment Criteria is marked as ‘NOT YET ACHIEVED’ you need to re-do this part of your assignment.
Command verbs
- You must understand exactly what the command verb is expecting of you and follow the instruction of the command verb carefully.
- Ignoring the command verb will likely lead you to fail this Assessment Criterion.
- From your portal, you can download your writing assignments’ Student Guide, which explains the meaning of the command verbs.
Assignment
- The assignments are part work-related and part theory related.
For example:
- FM Task 1 and Task 2 are theoretically related tasks, but you must write these AC from the perspective of an organisation using support points.
Formative feedback for your assignment
- We strongly advise that you submit a draft assignment.
- Your marker will judge your work against the Assessment Criteria.
- Your marker will give you written and verbal feedback on your draft assignment and suggest whether your work meets the standards.
Summative feedback for your assignment
- When submitting your ‘final’ assignment, the marker will judge your work against the Assessment Criteria.
- If you Achieve all ‘Pass’ criteria, you receive a Pass grade.
- If you Achieve all ‘Pass’ and all ‘Merit’ criteria, you receive a Merit grade.
- If you Achieve all ‘Pass’, all ‘Merit’ and all ‘Distinction’ criteria, you receive a Distinction grade.
- Internal Verifier will check a sample of your work to ensure that the marker accurately assesses the standard.
- As the External Verifier, ATHE will check that the Internal Verifier has checked the sample correctly.
- If all the checks show that your work meets the standards, you will be able to claim your certificate for you.
Plagiarism

Avoid malpractice
- Do your assignment on your own
- Read and research, but do not copy from other people, books or the internet (Plagiarism)
- Use the correct referencing system acknowledging the sources that you have used.
- Present work that contains correct, factual information
Plagiarism
- Definition:
- “To take and use as one’s own, the thoughts, writings or inventions of another.”
- Pretending that something is yours when it is not
- Plagiarism is not just about words but also ideas, data, images, photos …
- Can be intentional or unintentional
- It can be a result of poor note-taking
- It can be a result of carelessness with source information
- It can be caused by poor referencing
- It can be the reason for course failure!
- Use the Harvard Referencing system as explained in the Notes for Academic referencing
- uses plagiarism software to check your assignments.
- Plagiarised work will not be accepted for marking
- If in doubt … ASK
When dealing with information
Keep in mind:
- You need to keep an accurate record of all the sources you use in your work for Referencing purposes
- Tip: You can try using bibliography management software (also available on word documents)

Referring to Authors in your Assignment (in-text)
- Typical ways of introducing and discussing your literature sources:
- Author A (year of publication) claims/ states / reports/ suggests that…
- Author B (year of publication) further develops/opposes/ critiques the view that…
- Further evidence is needed when considering the theory of Author C (year of publication)…
Referring to the Authors in your Assignment, continued
Typical ways of citing your literature sources:
- According to Author D (year of publication)…
- Author E argues/ states/ reports that “… a long quotation should be included in a separate paragraph in single line spacing with indented margins …” (year of publication)
- Paraphrasing: It has been found that “…” (Author F, year of publication)
Use of Academic English in your Assignment
How can you link the data results with the literature? Typical ways of referring to sources in your assignments:
- When looking at [data source], it can be seen that…
- This [data source] clearly shows that…
- When comparing the [data source] results, it seems evident that…
[‘Data source’ is easily available information such as NSO, DOI, European Commission … or your original research.]
Typical ways of referring to graphs, tables or models
- Table 1 illustrates the growth/ the fall/ no change in…
- The diagram shows the impact of X on Y
- The information shown in Table 3/ Graph 4 applies to …
- Adopting the theory illustrated in Model 5, the organisation/ company/ institution will…
- Model 6 suggests that…
When referencing
- Cite your references clearly using the Harvard referencing system
- Look up the Notes for Academic Referencing guide and follow it
- Always keep note of your source/s
- Acknowledge all sources! In this way, you avoid plagiarism & academic malpractice
Book Referencing (in Bibliography)
The reference list should:
- Use the Harvard Referencing System
- The surname of the Author, the first letter of the name in capital.
- (Year of publication)
- Title
- Publisher
Example:
Kahneman, D. (2012) Thinking Fast and Slow. Penguin Books
Book Referencing (in Bibliography)
- Give as much information as possible
- Include the date the information was accessed
- The surname of the Author, the first letter of the name in capital.
- (Year of publication)
- Title
- EITHER Accessed on date from URL
- OR Available from URL accessed on date
Example:
Garrone, M. (2015) Do Startup Names Matter? [online] Accessed on 20-02-2019 from http://ideas.ted.com/do-startup-names-matter/
Get Organised

Assignment Writing
- A process with a structured approach

- Research the issues/arguments
- Gather information
- Organise & Write
- Presentation & Design
An ideal method for your assignment writing
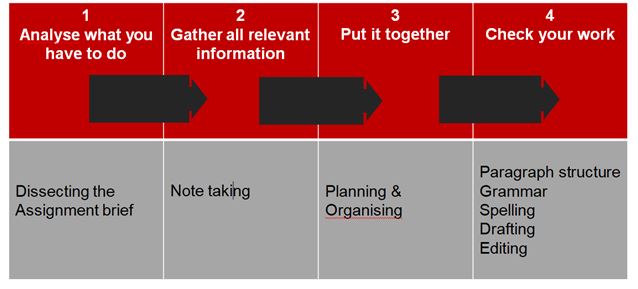
Instruction words
- Check your Writing Assignments Student guide, a dictionary online helps tools, and ask your tutor.
- It helps you to feel confident when you know what the market expects from you.
Putting it together – Writing up
- Convert your plan into a rough draft
- Work into a first draft
- Re-check that you are following the assignment brief
- Check that your line of argument flows (is logical)
- Concentrate on the most important issues at this stage
Remember…
- Clear objective = Clear focus
- Avoid dwelling on points not related directly to the objective (or not contributing significantly)
- Clear objectives facilitate the reading process – avoid long-winded and discursive writing.
Presentation

Presentation
Keep in mind that:
- Assignments are written for others to read, comment on and mark/grade/asses.
- If markers/assessors/tutors are to give you, the student, a fair and accurate assessment, they need to follow your work easily so they can concentrate on the content without the distractions of poor writing or disorganised presentation.
Presentation
Your submission should include:
- A cover sheet on page 1 of your assignment
- A Table of Contents
- An introduction
- The main text of the assignment (with various Headings)
- References (Include all your sources listed in alphabetical order by Author)
- Appendices
Presentation
The cover sheet or title page should include:
- Your name and surname
- Your student ID number
- The Unit name and number
- Word count
- Use headers or footers to include page numbering and your name and surname on every page
Presentation
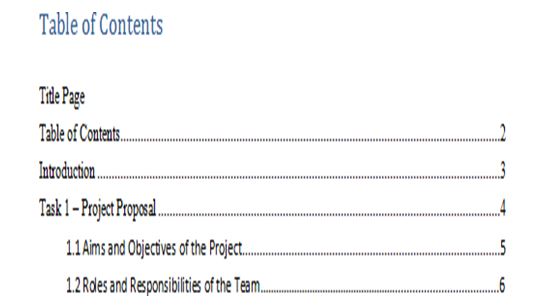
The Table of Contents should include:
- A list with the Headings and Sub-Headings
- In numbered format
- A list of Tables, Graphs and/or Figures (as needed)
- Tables, Graphs, and Figures should be titled individually and numbered separately
- References
- Appendices
- Titled individually and numbered (Heading title and number)
Table of Contents example:
Overall Structure
- Your assignment should be based on the assignment brief provided
- Introduction or Executive Summary (Task 1a)
- Give some background about yourself and the company you will be discussing (Do you work there? If not, why have you chosen another company? What is your role? What industry does it belong to? How many people work there? …)
Tasks – Sections
- Directly related to what has been asked of you from the assignment brief
- Number sections for ease of reference
- Ideally, no more than 3 levels, for example:
- Section 1
- Section 1.1
- Section 1.1.1
- It is suggested that you start each new Task on a new page
Paragraphs
- Keep short & simple
- Distinguish each fresh thought
- Ideally, two to four sentences long
- Double line spacing between paragraphs
Layout
- Visual appearance is vital in any written piece of work
- Easily readable assignments are written by students who
- Are organised
- Are professional
- Have clear and short explanations
- Follow the assignment brief
Managing Layout
- Spacing
- Margins
- Headings
- Sections
- Paragraphs
- Referencing
Whatever you choose, make it the same all throughout!
Managing layout suggestions
- Spacing
- 5 spacing indicates easier “follow through.”
- Margins
- Standard margins
- Justified makes documents look tidier
- Headings
- Improve layout & structure
- Anticipates what the section is all about
- Easier reading through the assignment
Page Numbering
- Always insert the page number
- Usually, numbers are at the bottom right of each page
- Typically the page numbers of the Title Page and Table of Contents are not counted but not visible. Thus the numbering starts from the introduction page
- Page numbering continues until the end of the document, including the bibliography and appendices.
Font and Size
- Do not use various fonts and different types of sizes and spaces as this creates an impression of messiness.
- Use the same font, size, space (between lines and paragraphs in the body of the assignment), and margins throughout your assignment.
- Avoid using difficult-to-read fonts and colours.
- Suggests the use of the Calibri font in size 11 or 12.
Charts & Graphs
- A picture says a thousand words

- Clarifies information
- Enhances comparisons
- Make reading easier and more fun. Think about using:
- Bar charts
- Pie charts
- Flow charts
- Organisational charts
Make your own – do not copy and paste!
A Reference list should:
- Be the section before the Appendix
- Include all your sources listed in alphabetical order by Author
Appendices
- Reserved for:
- The “data” on which observations are made
- The information on how you have reached certain decisions
- Any technical details
- Your work on Models, Frameworks and/or Theories
- It needs to be correctly referenced in the body of the assignment
- NOT the place for putting irrelevant material
- NOT an excuse for making the assignment bulkier & longer (it will NOT gain you marks)
- If you refer to it often, then its place is NOT in the appendix
- Rule of thumb = 1/3 of the assignment
Proofreading
- Pay close attention while writing your assignment, but after you finish writing, always proofread your work.
- Read your work aloud.
- Have a colleague read your work and point out any areas that seemed confusing
- Use computer-based tools such as Microsoft Word
- Scan your assignment for:
- Grammar, spelling and typing
- Consistent and appropriate language
- All sources of information cited
- Proper formatting
Use of Academic English

Assignment Writing – Use of Academic English
- Always write in the 3rd person, passive

- It was found…
- The article indicates…
- It is believed that…
- Be objective rather than subjective
- Use formal language
- Never use emotive language
Abbreviations
- Avoid abbreviating for laziness
- “Approx.”
- Implies to the reader that it is not worth bothering to write it out in full (how much is it worth reading then?)
- Organisations: mention the organisation in full (with an acronym in braces next to it) once. Then continue with acronyms across the document.
- For example European Union (EU)
Some Punctuation rules
- Capital letters, when required, only
- Names, Acts, Countries, Titles, Periods of History
- Acronyms
- God
- Use apostrophes only with the possessive clause
- For example, The organisation’s director …
- Do not use contractions (the shorter version). Always use the full form:
- It is, NOT it’s
Final tips
Avoid these Assignments fail points
- Bullet points can only be used very sparingly. You cannot answer an AC in bullet points.
- Do not copy & paste images of models/frameworks without an analysis
- Do not copy & paste images of statistics/data/information without a label. Reference it correctly.
- Text images, copied and pasted into the body of the assignment, still count towards the word count.
Success means that you …
- Attend all classes and take notes that make sense for you!
- Work on your assignment as you progress through your classes. Do not leave it to the last minute.
- Read and research the topic.
- Ask questions.
- Follow the assignment brief.
Thank You…..


